certbot Installation umziehen
December 14, 2025
certbot speichert die Zertifikate, Schlüssel und Konfigurationsdateien im Filesystem mit symbolischen Links. Beim Umzug auf eine neue Hardware gibt es zwei Varianten:
- certbot neu einrichten
- den certbot Ordner auf die neue Hardware umziehen.
Ich habe mich (natürlich aus Faulheit) für die Variante 2 entschieden, musste aber feststellen, dass es nicht ganz so einfach ist, symbolische Links auf eine neue Hardware mitzunehmen.
In meinem Fall (OS = Windows Server) half 7zip. Wenn man den certbot Ordner auf der alten Hardware einpackt, benutzt man als Archiv Typ <wim>.
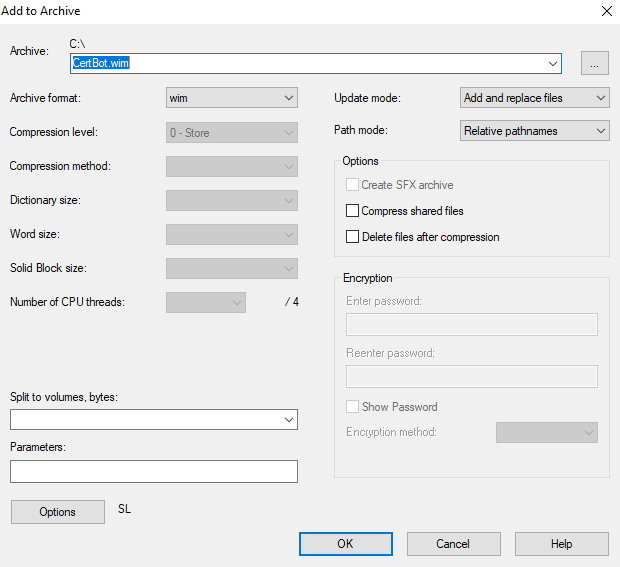
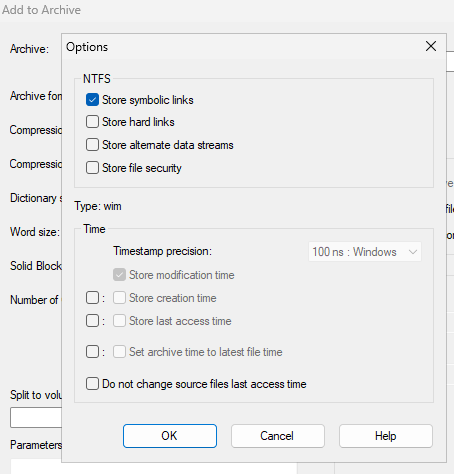
Im nächsten Schritt wählt man unter “Options” das Speichern der symbolischen Links.
Jetzt kommt die letzte Hürde. Beim Auspacken auf der Zielhardware werden die symbolischen Links zwar entpackt, allerdings wird statt dem Link die Datei abgelegt, auf die der Link verweist.
Die einzige Möglichkeit ist das Entpacken über die command line und die Nutzung der Option -snld. Die ist zwar nicht in der Kurzhilfe zu finden (siehe unten), funktioniert aber hervorragend.
7-Zip 25.01 (x64) : Copyright (c) 1999-2025 Igor Pavlov : 2025-08-03
Usage: 7z […] […] [@listfile]
a : Add files to archive
b : Benchmark
d : Delete files from archive
e : Extract files from archive (without using directory names)
h : Calculate hash values for files
i : Show information about supported formats
l : List contents of archive
rn : Rename files in archive
t : Test integrity of archive
u : Update files to archive
x : eXtract files with full paths
— : Stop switches and @listfile parsing
-ai[r[-|0]][m[-|2]][w[-]]{@listfile|!wildcard} : Include archives
-ax[r[-|0]][m[-|2]][w[-]]{@listfile|!wildcard} : eXclude archives
-ao{a|s|t|u} : set Overwrite mode
-an : disable archive_name field
-bb[0-3] : set output log level
-bd : disable progress indicator
-bs{o|e|p}{0|1|2} : set output stream for output/error/progress line
-bt : show execution time statistics
-i[r[-|0]][m[-|2]][w[-]]{@listfile|!wildcard} : Include filenames
-m{Parameters} : set compression Method
-mmt[N] : set number of CPU threads
-mx[N] : set compression level: -mx1 (fastest) … -mx9 (ultra)
-o{Directory} : set Output directory
-p{Password} : set Password
-r[-|0] : Recurse subdirectories for name search
-sa{a|e|s} : set Archive name mode
-scc{UTF-8|WIN|DOS} : set charset for console input/output
-scs{UTF-8|UTF-16LE|UTF-16BE|WIN|DOS|{id}} : set charset for list files
-scrc[CRC32|CRC64|SHA256|SHA1|XXH64|*] : set hash function for x, e, h commands
-sdel : delete files after compression
-seml[.] : send archive by email
-sfx[{name}] : Create SFX archive
-si[{name}] : read data from stdin
-slp : set Large Pages mode
-slt : show technical information for l (List) command
-snh : store hard links as links
-snl : store symbolic links as links
-sni : store NT security information
-sns[-] : store NTFS alternate streams
-so : write data to stdout
-spd : disable wildcard matching for file names
-spe : eliminate duplication of root folder for extract command
-spf[2] : use fully qualified file paths
-ssc[-] : set sensitive case mode
-sse : stop archive creating, if it can’t open some input file
-ssp : do not change Last Access Time of source files while archiving
-ssw : compress shared files
-stl : set archive timestamp from the most recently modified file
-stm{HexMask} : set CPU thread affinity mask (hexadecimal number)
-stx{Type} : exclude archive type
-t{Type} : Set type of archive
-u[-][p#][q#][r#][x#][y#][z#][!newArchiveName] : Update options
-v{Size}[b|k|m|g] : Create volumes
-w[{path}] : assign Work directory. Empty path means a temporary directory
-x[r[-|0]][m[-|2]][w[-]]{@listfile|!wildcard} : eXclude filenames
-y : assume Yes on all queries